UR Robotic Arm
Configured the UR5e robot arm, Robotiq-2f-85 gripper, 3D-Connexion teleoperation from scratch while working at MiLab and applied them to conduct research on manipulation. You can find the repo here !
- ⚙️ Important Things
- ⚙️ Setting | UR5e
- ⚙️ Setting | Gripper | Robotiq-2f-85
- ⚙️ Setting | Teleoperation | 3D Connexion
- ⚙️ Coding
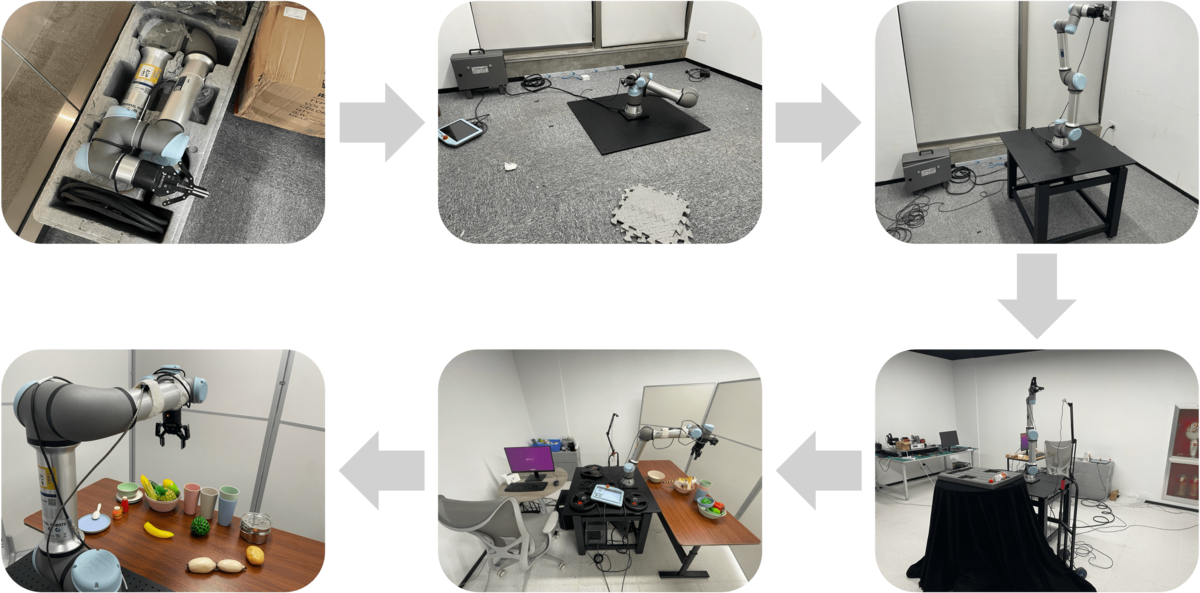 The construction process of the hardware platform.
The construction process of the hardware platform.
⚙️ Important Things
Grab before Start
- ROS
Robot Operating System (ROS)is an open-source framework for robot software development. It provides tools and libraries to help developers create robot applications. ROS enables communication between various parts of a robot system, supports hardware abstraction, and includes utilities for building, debugging, and visualizing robotic systems. - Melodic (Ubuntu 18.04)
ROS Melodic Moreniais a version of the Robot Operating System tailored for Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver). It includes long-term support and a stable set of libraries and tools for developing and deploying robot applications. Melodic is known for its compatibility and reliability on Ubuntu 18.04. - Neotic (Ubuntu 20.04)
ROS Noetic Ninjemysis a version of the Robot Operating System designed for Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa). It is the latest LTS (Long-Term Support) release of ROS 1, featuring updated libraries and tools that leverage improvements in the Ubuntu 20.04 environment. Noetic aims to provide enhanced stability and performance for modern robotic applications. - Moveit
MoveItis an open-source software for robotic motion planning, manipulation, 3D perception, kinematics, control, and navigation. It is widely used in the ROS ecosystem to enable advanced robotic behaviors, providing tools for collision detection, inverse kinematics, and motion planning, as well as integration with various robotic hardware and simulation environments. - URDF
URDF (Unified Robot Description Format)files are XML files used in ROS to describe a robot’s physical configuration. URDF files define the structure, visual representation, and physical properties of a robot model, including links (rigid bodies), joints (connections between links), and their properties such as dimensions, mass, and inertial properties. - Gazebo
Gazebois a powerful simulation tool used in robotics. It provides a realistic environment where you can test and develop robots without needing physical hardware. With Gazebo, you can create complex robot models, simulate sensors, and visualize how robots interact with their surroundings. This helps in designing and debugging robot behavior in a safe and cost-effective way. - RViz
RViz (Robot Visualization)is a tool used to visualize the data coming from a robot’s sensors and state. It is commonly used in conjunction with the Robot Operating System (ROS). RViz helps developers see what the robot is “seeing,” such as its surroundings, sensor data, and the robot’s planned movements. This visualization is crucial for debugging and understanding the robot’s behavior in real time. - URCap
URCapis an extension platform for Universal Robots (UR) robotic arms. It allows developers to create custom software plugins that can be installed on UR robots. These plugins can enhance the functionality of the robot, making it easier to integrate with other equipment, add new features, and customize user interfaces. - RTDE
RTDE (Real-Time Data Exchange)is a communication protocol used by Universal Robots (UR) robotic arms. It enables real-time exchange of data between the robot controller and external systems. With RTDE, you can send commands to the robot, receive sensor data, and monitor the robot’s status with low latency, ensuring precise and timely control. - URScript
URScriptis a scripting language provided by Universal Robots (UR) for programming and controlling UR series robotic arms. It allows users to write scripts to directly control the robot’s movements, I/O operations, and other functionalities. - Python-urx
urxis a python library to control the robots from Universal Robots. It is published under the LGPL license and comes with absolutely no guarantee.
⚙️ Setting | UR5e
🔩 Drive with Ros
1. Environment
- UR5e
- Ubuntu 20.04.6
- Noetic
- Python3.8
2. Intall ROS | Noetic | Ubuntu 20.04
#
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
# (or maybe we need the following due to the firewall)
# sudo sh -c '. /etc/lsb-release && echo "deb http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ros/ubuntu/ `lsb_release -cs` main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
#
sudo apt install curl # if you haven't already installed curl
curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ros/rosdistro/master/ros.asc | sudo apt-key add -
#
sudo apt update
#
sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full
#
sudo apt search ros-noetic
#
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash
echo "source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
#
sudo apt install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rosinstall-generator python3-wstool build-essential
sudo apt install python3-rosdep
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
3. Install moveit
sudo apt install ros-noetic-moveit
4. Install universal_robots_ros_driver
Binary-Version
# we set ${ROS_DISTRO} as noetic
sudo apt install ros-noetic-ur-robot-driver
sudo apt install ros-noetic-ur-calibration
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-universal-robots
# set the source
source /opt/ros/${ROS_DISTRO}/setup.bash
Development-Version
# source global ros
source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash
# create a catkin workspace
mkdir -p catkin_ws/src && cd catkin_ws
# clone the driver
git clone https://github.com/UniversalRobots/Universal_Robots_ROS_Driver.git src/Universal_Robots_ROS_Driver
# clone the description.
git clone -b noetic-devel https://github.com/ros-industrial/universal_robot.git src/universal_robot
# install dependencies
sudo apt update -qq
rosdep update
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -y
# build the workspace
catkin_make
# activate the workspace (ie: source it)
source devel/setup.bash
#@NOTICE : we need use the python/boost/... from ubuntu20.04 rather than anaconda
$ sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
#@NOTICE : remove the initialization of anaconda or any other environments
5. Simulation Test
# simulate the robot and environment in Gazebo
roslaunch ur_gazebo ur5e_bringup.launch
# use MoveIt for motion planning and control
roslaunch ur5e_moveit_config moveit_planning_execution.launch sim:=true
# finally visualize the whole process through RViz
roslaunch ur5e_moveit_config moveit_rviz.launch
6. Install External-Control on robot | link PC and robot through TCP-IP
###### CONNECT ROBOT and PC ######
# the PC IPv4
address : 192.168.1.10
netmask : 255.255.255.0
gateway : 192.168.1.1
# the robot IPv4
address : 192.168.1.60
netmask : 255.255.255.0
gateway : 192.168.1.1
7. Communicate with the Robot | rs485
# launch the ros score
roslaunch ur_robot_driver ur5e_bringup.launch use_tool_communication:=true tool_voltage:=24 tool_parity:=0 tool_baud_rate:=115200 tool_stop_bits:=1 tool_rx_idle_chars:=1.5 tool_tx_idle_chars:=3.5 tool_device_name:=/tmp/ttyUR
# test the ttyUR connection
rosrun ur_robot_driver tool_communication
# utilize just like the true serial
rosrun imaginary_drivers rs485_node device:=/tmp/ttyUR
8. Prepare the ROS PC
Extract calibration information
roslaunch ur_calibration calibration_correction.launch robot_ip:=192.168.1.60 target_filename:="home/robot/my_robot_calibration.yaml"
9. Get Start
Notice : the version of URSoftware for e-series robots should no less than 5.5.1, if not we can update the software version of the UR pad through updates
- Starting the driver and visualizing the robot in RViz
- Control the robot
- Control the robot using MoveIt
###### Visualizing ######
# launch the driver
roslaunch ur_robot_driver ur5e_bringup.launch robot_ip:=192.168.1.60 kinematics_config:=/home/robot/my_robot_calibration.yaml
# in another terminal run rviz for visualization
roslaunch ur_robot_driver example_rviz.launch
###### Controling ######
rosrun ur_robot_driver test_move
###### Control the robot using Moveit ######
roslaunch ur_robot_driver ur5e_bringup.launch robot_ip:=192.168.1.60 kinematics_config:=/home/robot/my_robot_calibration.yaml
roslaunch ur5e_moveit_config moveit_planning_execution.launch
roslaunch ur5e_moveit_config moveit_rviz.launch rviz_config:=/home/robot/ur5e_ws/src/universal_robot/ur5e_moveit_config/launch/moveit.rviz
🔩 Drive with Python-urx
⚙️ Setting | Gripper | Robotiq-2f-85
1. Robotiq Environment
# # official - only support until Melodic
# git clone https://github.com/ros-industrial/robotiq.git src/robotiq
# support for Noetic
git clone https://github.com/jr-robotics/robotiq.git src/robotiq
# install dependencies
sudo apt update -qq
rosdep update
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -y
# build the workspace
catkin_make
# activate the workspace (ie: source it)
source devel/setup.bash
2. Connection
Method-1
2f-85 \(\rightarrow\) rs485 \(\rightarrow\) usb \(\leftarrow\) computer
Method-2
2f-85 \(\rightarrow\) rs485 \(\rightarrow\) tool communication \(\leftarrow\) computer
Method-3
2f-85 \(\rightarrow\) rs485 \(\rightarrow\) usb \(\rightarrow\) pendant \(\leftarrow\) 65332 \(\leftarrow\) computer
3. Run
# test the conection by Method-1
sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER
dmesg | grep tty
#
roscore
# run the node
rosrun robotiq_2f_gripper_control Robotiq2FGripperRtuNode.py /dev/ttyUSB0
# run the controller
rosrun robotiq_2f_gripper_control Robotiq2FGripperSimpleController.py
# run the listener
rosrun robotiq_2f_gripper_control Robotiq2FGripperStatusListener.py
⚙️ Setting | Teleoperation | 3D Connexion
1. Env Setting
ur_rtdespnavrobotiq gripper+3D Connexion spacemouse+ur5e
2. Build
- download dependencies of spacemouse
sudo apt install libspnav-dev spacenavd; sudo systemctl start spacenavd pip install spnav - check if spacemouse is connected to workstation
lsusb - download RTDE library
pip install ur_rtdeIn the
spnavlibrary,PyCObject_AsVoidPtris deprecated.find . -name spnavon terminal to findspnavfolder. Replace all instances ofPyCObject_AsVoidPtrwithPyCapsule_GetPointerininit.py
⚙️ Coding
- ROS (Robotics Operating System)
- tutorial
🔧 Rospy Intro From GPT
- Initialize a ros
Noderospy.init_node('node_name', anonymous=True) - Publish the
msgrospy.Publisher('chatter', String, queue_size=10) - Subscribe the
msgrospy.Subscriber('chatter', String, callback) - Utilize the
serviceServersiderospy.Service('add_two_ints', AddTwoInts, handle_add_two_ints)Clientsiderospy.wait_for_service('add_two_ints')rospy.ServiceProxy('add_two_ints', AddTwoInts)
🔧 Debug
# show all of the topic we can use
rostopic list
# show a specific topic
rostopic info /topic_name
rostopic echo /topic_name
rostopic type /topic_name
# show the communication graph
rqtgraph
